
In recent times, we have seen the explosion of interest in data-driven HR insights, and it is not just hype; it is a significant shift that is transforming how organizations view their most important asset: their people. HR leaders today are faced with unrelenting pressure to apply more than their intuition, to quantify the workforce impact, to forecast future talent needs, and to tailor the employee experience. Let’s be honest, there are many HR functions that can leverage AI, and now, with this new environment, especially with decision-making driven by data, presents an opportunity for AI in HR analytics.
Forget the old view of HR packed full of administrative work. As proven by a study from MIT, connecting AI tools for professionals can increase productivity by an insane 60%. This is not about job loss; it is about building human capabilities and providing HR pros time to work on valuable, strategic activities. The global AI in HR leverage market is roughly $5.03 billion in 2025 and projected to be $9.52 billion by 2030, so this is a massive transition! HR teams everywhere are dealing with administrative loads and reporting expectations while keeping pace with their peers, who are heaping strategic asks on them. AI can be a huge opportunity, as many employees would like to shed their “grunt work” with the assistance of AI and focus on more strategic or creative work.
This article delves into how meticulously crafted AI prompts, specifically designed for AI in HR analytics, can unlock unprecedented insights, and we guarantee that if you use these prompts, you’ll see much higher productivity.
What Makes a High-Impact AI Prompt for HR Analytics?
To obtain quality actionable insights from AI tools like ChatGPT or Gemini for use in HR analytics, prompts must be constructed carefully. You can think of this as giving the AI a template to follow; your goal is to obtain not just data from the AI, but knowledgeable insights. The O-C-F Framework is top of mind; it has been praised by the likes of Sam Altman (CEO of Open AI):
- Objective: Establish precisely what you want the AI to do (e.g., determine trends, forecast attrition, segment employee data, summarize a report).
- Context: Provide background (e.g., applicable datasets, organizational culture, specific challenges, intended audience for insights).
- Format: Make it clear how you want the response to be reported back (e.g., table, code with description in Mermaid, bulleted list, narrative summary).
Best Practices for Prompting AI in HR Analytics:
- Implement the Most Current Models: Use the most powerful and current models (e.g. the ChatGPT-4-o) for detailed analysis capabilities.
- Iterate and Refine (Prompt Chaining): Use these initial prompts as a starting point and iterate through commands one after the other to narrow, expand, or dig deeper.
- Clearly State Data Sources and Formats: Clearly state the data you are providing or referring to, how it is structured (rows and columns), and which columns are the primary focus (e.g., “Position Type”, “Employee Type”, “Status”, “Position Title”, and “Total Compensation”).
- Set Boundaries and Exclusions: Set clear boundaries for what you will analyze (e.,g. “do not include data for new hires in the past three months”).
- Use Business Questions: Frame prompts around specific business questions/issues HR is looking to solve.
AI’s Transformative Impact on the Employee Journey and Its Data
As we progress through 2025, the collaboration between advanced AI models and effective prompts is fundamentally reshaping every aspect of the employee journey. The employee journey creates a feeder of data that can be analyzed by AI in a way that instigates continuous improvement in the cycle of AI in HR analytics:
- Personalized Onboarding: AI recommends a tailored onboarding plan based on data from the new hire and then provides data back on onboarding effectiveness.
- Personalized Development: AI will analyze data about past performance (alongside future aspirations) to determine the best training solutions that track the impact of learning.
- Proactive Well-being: AI analyzes data about sentiment and behavior to recognize patterns that could indicate early distress signals like burnout, and act before it escalates.
- Optimized Internal Talent Mobility: AI suggests opportunities for internal mobility that fit the organization’s need for skills and experience so that the need for external recruitment diminishes.
In the end, AI creates a responsive workplace that prioritizes the human experience, but its greatest strengths can be seen in the data it collects and analyzes, and uses to improve. The continuous flow of information is critical for successful AI in HR analytics.
What Happens If You Keep Using Poor Prompts in HR Analytics?
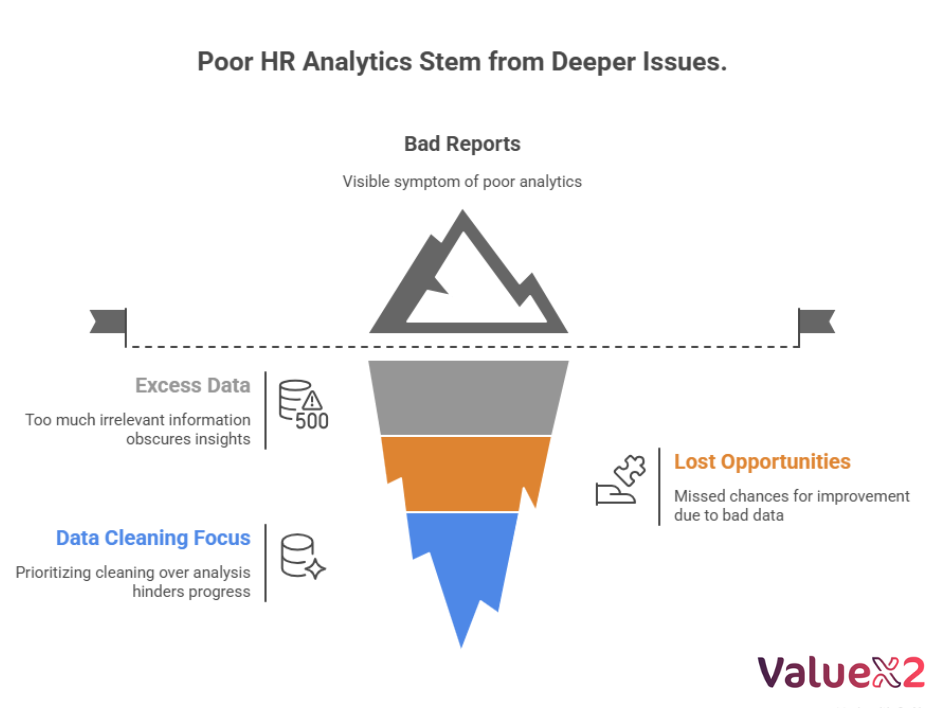
Generative AI, especially within HR analytics, is incredibly promising. Yet, poorly designed prompts have negative consequences:
- Excess or Useless Data: If your prompt is too vague, the AI will unearth so much data that you won’t be able to use it.
- Bad Reports: If a prompt does not contain enough context or clear definitions, you can expect incorrect reports that result in misinformed decisions that are often high stakes.
- Lost Opportunities: Prompts that do not have enough detail prompt the AI to produce low-quality reporting that only recounts a few shifted patterns instead of more substantial and complex patterns.
- Focus on Cleaning Data instead of Analysing Data: Inadequate prompts can refocus the user from strategic focus on analysis while spending time on data preparation.
The following prompts are designed to highlight vague prompts so the AI can start producing raw HR data into planned action intelligence using the latest HR analytics AI advances.
Powerful AI Prompts for HR Analytics & Continuous Improvement
The true power of AI in HR analytics lies in its ability to quickly process vast datasets, identify patterns, and generate actionable insights.
Table 1: Recruitment & Talent Acquisition Analytics with AI
| Topic | AI Prompt Example | Why It Works |
| Time-to-Hire Bottleneck Analysis | “Using the attached recruitment funnel data (CSV, with the following columns: Application_Date, Screen_Date, Interview_HM_Date, Panel_Interview_Date, Offer_Date, Accepted_Date, Role_ID, Department), identify all stages where candidates are taking an average of more than 25% longer than the average time in the previous quarter to progress through this stage. For each identified slow stage, identify one potential root cause, and two practical, no-cost solutions to test for improvement. Prepare and present your findings in a table with the following Columns: Slow Stage, Average Duration (Days), Previous Quarter Avg (Days), Potential Root Cause, Suggested Solutions.” | This prompt pinpoints recruitment inefficiencies by comparing performance against a benchmark, a core function of AI in HR analytics. It moves beyond data identification to offer proactive, testable solutions, fostering an Agile HR mindset. This translates directly into faster, more efficient hiring processes. |
| Quality-of-Hire KPI Definition & Data Source Mapping | “Identify four key Quality-of-Hire (QoH) key performance indicators for our ‘Software Engineer’ roles. Provide a calculation formula for each KPI and identify the specific HR system(s) (e.g., ATS, HRIS, Performance Management System, LMS) where the raw data used for the KPI’s calculation is located. Also, propose one possible AI prompt that could be leveraged to automate the calculation or reporting of each KPI. Assume we are driving to hire candidates who perform well and stay with the organization a long time.” | This elevates HR to strategic measurement by defining key metrics and mapping data sources, crucial for robust AI in HR analytics. Including AI prompts for automation demonstrates a tech-forward approach, maximizing by making analytics both efficient and impactful. |
| AI in Recruiting & Talent Acquisition | “Now that we’ve attached a CSV file containing columns Candidate_ID, Source (eg. LinkedIn, Referral), Hire_Status (Hired/Not Hired), Time_to_Hire_Days, and First_Year_Performance_Rating (1-5 scale for hired candidates), we’d like you to look into which 3 sources produce the highest quality candidates (high performance rating and lower time-to-hire) and the 2 sources with the lowest conversion rates to Hired. Provide a summary of your findings in bullet points, and then provide recommendations for optimizing our talent acquisition budget allocation for the next quarter based on the data.” | This optimizes recruitment spend by identifying effective channels, combining multiple metrics for a holistic view. The recommendation for budget optimization directly translates data into strategic business decisions, demonstrating tangible results delivered through AI in HR analytics. |
| Predicting Candidate Success based on Interview Data | “Assume a dataset of past candidates, including Pre-Interview Assessment Scores, Interview Panel Scores (average), and Post-Hire Performance Rating (1-5 scale after 6 months). Describe how an AI model could predict the likelihood of a new candidate achieving a ‘High Performance Rating’ (4 or 5) based on their assessment and interview scores. Outline key data points, recommended AI model, ethical considerations regarding bias, and a high-level pseudo-code or conceptual algorithm.” | This prompt pushes into predictive analytics, a cornerstone of advanced AI in HR analytics. It seeks a conceptual framework and addresses ethical considerations, highlighting a responsible and forward-thinking approach to AI in driving future-oriented decisions. |
Table 2: Workforce Planning & Talent Mobility Analytics with AI
| Topic | AI Prompt Example | Why It Works |
| Skill Gap Identification & Training Recommendation | “Review the attached CSV file with Employee_ID, Department, Current_Skills (in list format), Performance_Rating (1-5), Future_Strategic_Goals (text description for each department). Identify important skill gaps at the departmental level that could impact departments in achieving the Future Strategic Goals? For the top 3 skill gaps identified, recommend a specific micro-learning course (with fictitious title and topics for the course) as well as an applied project idea that would help to close this gap in the next 90 days. In a table: Department, Strategic Goal Impacted, Identified Skill Gap, Recommended Micro-Learning, Project Idea.” | Pinpoint key skill gaps at the departmental level that could prevent future strategic goals from being achieved. For the top 3 skill gaps found, suggest a particular micro-learning course (with hypothetical title and topics) and a hands-on project idea that can close this gap in 90 days. Report in a table: Department, Strategic Goal Impacted, Identified Skill Gap, Recommended |
| Attrition Risk Prediction for High-Performers | “Given a dataset (conceptual, describe attributes) of current employees, including Tenure, Performance_Rating, Compensation_vs_Market, Last_Promotion_Date, Engagement_Survey_Score, and Manager_Sentiment_Score, describe how an AI model could identify ‘High Risk’ of voluntary attrition, specifically for ‘High Performance Rating’ employees (4 or 5). Outline key features AI would weigh, predictive model type, and how HR could proactively intervene. Conclude with two actionable, non-monetary retention strategies personalized by risk factors.” | This prompt focuses on proactive retention of critical talent, a high-value HR function enabled by AI in HR analytics. It explores predictive modeling and outlines potential interventions, emphasizing non-monetary strategies for holistic employee well-being and engagement, delivering by preventing costly turnover. |
| Internal Mobility Opportunity Matching | “Based on an employee skills inventory (conceptual dataset: Employee_ID, Skills_List, Project_Experience, Career_Aspirations) and a list of open internal roles (Role_ID, Required_Skills, Project_Context), generate a ranked list of the top 5 internal candidates for a ‘Data Scientist’ role. For each candidate, explain why they are a strong match, highlighting specific skills and experiences. Also, identify any minor skill gaps and suggest a quick learning path to bridge them. Present this as a prioritized list.” | This streamlines internal talent allocation, promoting growth and reducing external hiring costs. It moves beyond simple keyword matching to explain the ‘why,’ fostering trust in AI in HR analytics-driven insights. Identifying skill gaps and suggesting learning paths promotes continuous development, a core tenet of modern HR. |
Table 3: Employee Engagement & Experience Analytics with AI
| Topic | AI Prompt Example | Why It Works |
| Analysis of Employee Engagement | “Analyze the free-text employee feedback data attached to our last ‘Work-Life Balance’ pulse survey (pretend each entry is a brief paragraph). Categorize sentiment as ‘Positive’, ‘Neutral’, or ‘Negative’. Determine the top 3 repeated themes among ‘Negative’ feedback, and list 2-3 representative quotes for each. Lastly, suggest one actionable initiative for each negative theme that HR could adopt to enhance work-life balance over the next quarter. Do this in a summary report with themes and initiatives.”“ | This question utilizes AI for sentiment analysis, pulling structured insights from unstructured text. It moves beyond classification to recognize actionable themes and recommend tangible initiatives, facilitating a data-driven process for enhancing employee experience, a key element of AI in HR analytics. The emphasis on near-term initiatives aligns with Agile principles. |
| Correlation Between Engagement Scores & Performance | “Given historical data (conceptual dataset) with Employee_ID, Quarterly_Engagement_Score, and Quarterly_Performance_Rating (1-5 scale), identify if there is a statistically significant correlation between higher engagement scores and higher performance ratings across all departments over the past year. If correlation exists, describe its strength and provide 3 actionable strategies for managers to foster engagement, specifically targeting behaviors that have shown a positive correlation. If no significant correlation is found, explain potential reasons and suggest alternative metrics to analyze.” | This question propels you to try to measure the effect of engagement on performance, a critical business performance metric. It requires a scientific, evidence-based method of HR intervention and looks for alternative analytical directions in case initial assumptions are not backed by facts, enabling agility and reasoning using AI in HR analytics. |
| Tailored Communication Strategy Based on Segmented Data | “Suppose our workforce is divided into ‘Frontline Employees’, ‘Office-Based Professionals’, and ‘Remote Tech Team’. From the attached aggregated engagement survey results (aggregated data for each segment, noting top 3 concerns and top 3 satisfaction areas), prepare three separate internal communication messages (one for each segment) announcing new well-being initiatives. Each message must be customized in terms of tone and content to tackle specific concerns and capitalize on satisfaction points, and must not exceed 150 words.” | This question emphasizes the strength of data segmentation in facilitating highly targeted HR interventions. It illustrates how AI may be used to help build subtle communications that resonate with various groups of employees and extend the impact of HR initiatives. This is a hands-on use of AI in HR analytics to improve employee experience. |
Table 4: HR Operations & Efficiency Analytics with AI
| Topic | AI Prompt Example | Why It Works |
| Payroll Discrepancy Detection & Anomaly Reporting | “Based on the rolling monthly payroll data for 6 months (conceptual dataset: Employee_ID, Department, Gross_Pay, Overtime_Hours, Deductions, Net_Pay), identify employee monthly records with Net_Pay +10/-10% of their average Net_Pay over the last 5 months, excluding new hires in their first month. For each obvious anomaly, indicate the Employee_ID, Month_of_Anomaly, and Deviation_Percentage. Provide some sample reasoning for the irregularities, e.g., excessive amount of overtime, changes in benefits, and data entry errors. Present this as an anomaly report.” | This prompt supports HR operational efficiency by automating anomaly detection in critical processes like payroll, a direct application of AI in HR analytics. It frees HR teams from manual reconciliation and allows them to focus on investigating genuine discrepancies, minimizing errors, and ensuring compliance. The suggested reasons for deviation accelerate troubleshooting. |
| HRIS Data Quality Audit & Recommendations | “Assume the role of an HR Data Auditor. Review the attached sample of our HRIS data (small CSV, contains Employee_ID, Date_of_Birth, Hire_Date, Job_Title, Manager_ID, Department_ID) and identify any potential data quality problems, including missing values, inconsistent format, and logical inconsistencies (e.g, Date_of_Birth implies employee is too young). For each problem that you identify, state the column, the problem type, and determine a data cleaning rule or process change to avoid the problem in the future. Order the problems by how significant they are likely to be when it comes to tthe accuracy of HR predictive analytics. Write your findings and recommendations.” | Clean data is the foundation of effective AI in HR analytics. This prompt leverages AI to proactively identify data quality issues, which often plague HR systems. By suggesting preventative measures, it contributes to long-term data integrity and more reliable analytical insights. |
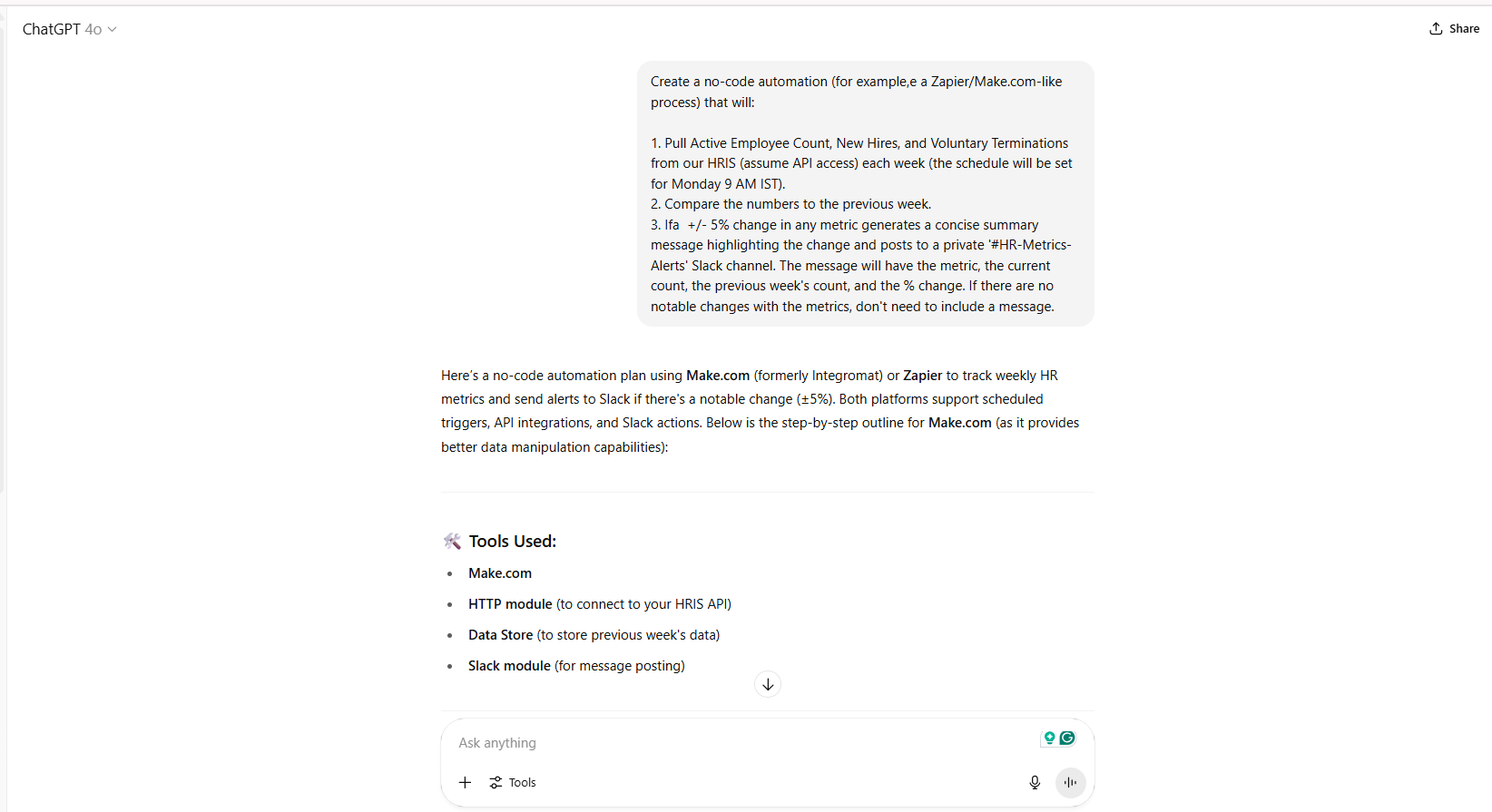
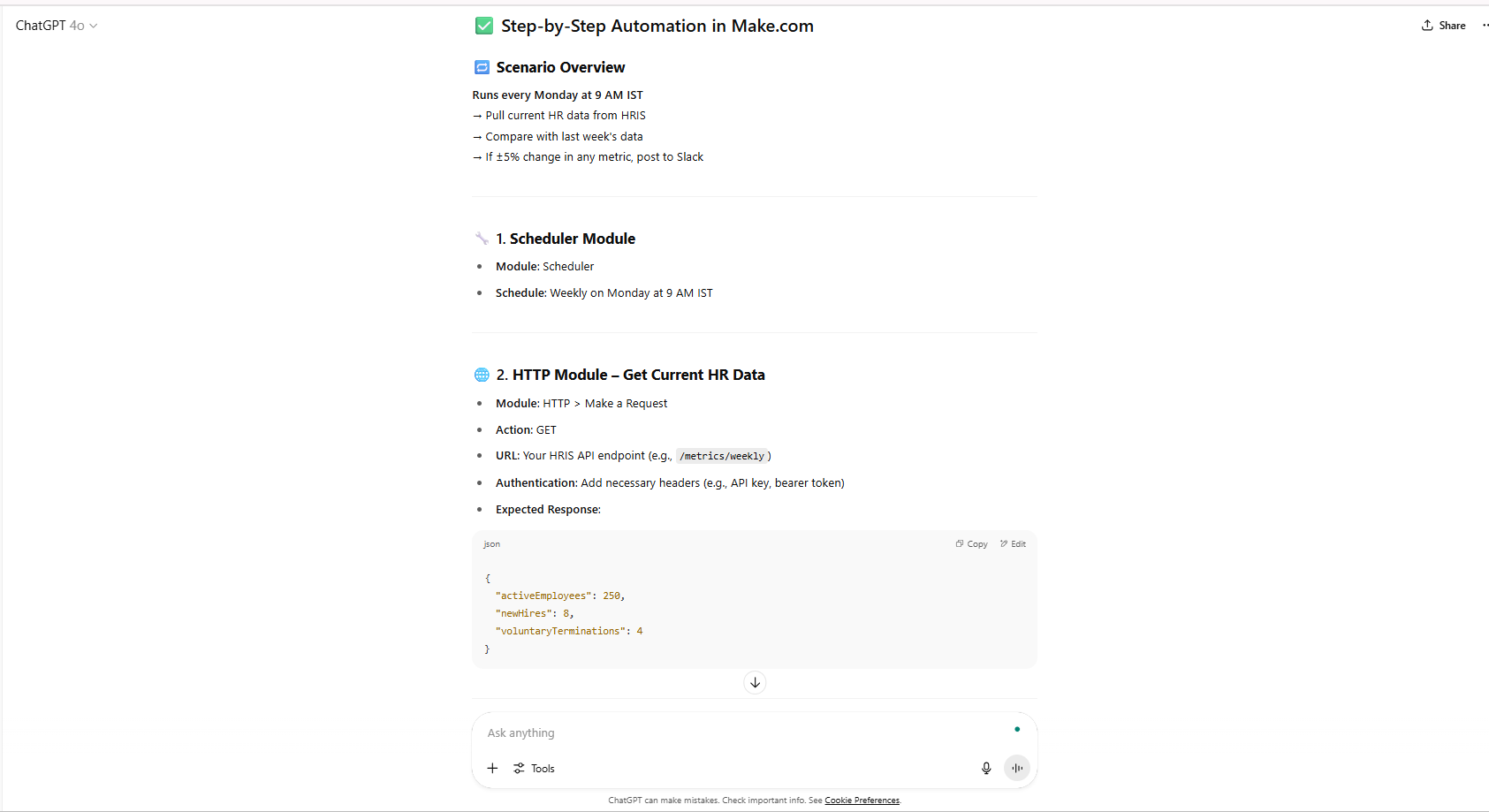
| Automation Workflow for Key HR Metrics Dashboard | “Create a no-code automation (for example,e a Zapier/Make.com-like process) that will:1. Pull Active Employee Count, New Hires, and Voluntary Terminations from our HRIS (assume API access) each week (the schedule will be set for Monday 9 AM IST). 2. Compare the numbers to the previous week.
3. Ifa +/- 5% change in any metric generates a concise summary message highlighting the change and posts to a private ‘#HR-Metrics-Alerts’ Slack channel. The message will have the metric, the current count, the previous week’s count, and the % change. If there are no notable changes with the metrics, don’t need to include a message.” |
It encompasses the essence of Agile HR by automating the constant, real-time observations of key metrics. You remove the manual reporting work for HR and give them space to interpret and to act. The threshold-based alerts will notify you of only high-impact and/or high contribution changes. You save time and can act earlier when AI assists HR professionals in analytics.. |
Table 5: DEI (Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion) Analytics with AI
| Topic | AI Prompt Example | Why It Works |
| Gender Pay Gap Analysis & Drivers | “Refer to the compensation data attached (CSV of Employee_ID, Gender, Department, Job_Level, Base_Salary, Total_Compensation, Tenure_Months, Performance_Rating). Average the gender pay gap (the percentage difference of Total_Compensation by gender) in each combination of Department and Job_Level. If any Department and Job_Level combination has a gap of greater than 5% and does favor one gender, identify two potential non-discriminatory causes of the gap (I.,. Tenure differences, distribution of performance ratings, etc.). Propose a data-driven action that HR could take for each significant gap identified. The project should be presented as a simple report.” | This prompt directly addresses a critical DEI metric – the gender pay gap – and goes beyond simple reporting to seek potential drivers. By suggesting data-driven actions, it empowers HR to create targeted interventions for promoting equity. This is a powerful demonstration of how AI in HR analytics can support by fostering a more equitable workplace. |
| Diversity in Leadership Pipeline Analysis | “Given our internal talent pipeline data (conceptual dataset: Employee_ID, Current_Job_Level, Gender, Ethnicity, Years_in_Current_Level, Identified_as_High_Potential), analyze the representation of Gender and Ethnicity at each successive Job_Level (e.g., Entry, Mid, Senior, Leadership). Identify any significant drop-off points or plateaus in representation. For any two such critical points, hypothesize a potential systemic barrier and suggest a data-driven intervention (e.g., targeted mentorship, unconscious bias training, revised promotion criteria) to improve diversity in leadership. Present as a clear analysis with recommendations.” | This prompt enables granular analysis of diversity representation across career stages, revealing potential systemic barriers. By prompting for both hypotheses and data-driven interventions, it helps HR proactively build a more inclusive leadership pipeline, directly contributing to organizational agility and long-term success through AI in HR analytics. |
| Inclusive Language Audit for Job Descriptions | “Review the attached sample job description for a ‘Marketing Manager’. Identify any language that might inadvertently contribute to gender bias, age bias, or exclusionary language. For each identified instance, suggest a more inclusive alternative phrasing. Additionally, propose three general best practices for writing inclusive job descriptions based on this exercise. Present the original phrases, suggested alternatives, and best practices.” | While not strictly “analytics,” this prompt demonstrates how AI can be used to audit existing HR content for DEI compliance and best practices. It’s a proactive step in fostering an inclusive environment from the very first touchpoint with candidates, ultimately impacting candidate diversity and the data collected, a supportive role for AI in HR analytics. |
These are some of the interesting results that we received after trying one of the prompts.
 Is Agile HR Best for Analytics?
Is Agile HR Best for Analytics?
The true transformative power of these AI prompts is unleashed when paired with Agile HR methodologies. Agile HR embraces short, iterative “sprints,” visible “backlogs,” daily “stand-ups, and transparent “retrospectives.” This cadence perfectly complements Generative AI, enhancing AI in HR analytics:
- Prompt Creates Data: An AI prompt generates an analytical report or identifies a data pattern in hours.
- Retro Examines Data: During a retrospective, the HR team immediately reviews AI-generated insights, discusses findings, and identifies next steps.
- Next Sprint Tests Improvement: Insights from AI and the retrospective directly feed into the next Agile sprint, allowing rapid testing of small, measurable improvements.
This creates a powerful “analytical flywheel”—a continuous feedback loop of AI-powered insights, Agile iteration, and measurable impact—allowing HR to become truly data-driven, responsive, and strategic.
The true transformative power of these AI prompts is unleashed when paired with Agile HR methodologies. Agile HR embraces short, iterative “sprints,” visible “backlogs,” daily “stand-ups, and transparent “retrospectives.” This cadence perfectly complements Generative AI, enhancing AI in HR analytics:
- Prompt Generates Data: An AI prompt generates an analytical report or identifies a data pattern in hours.
- Retrospective Examines Data: During a retrospective, the HR team immediately reviews AI-generated insights, discusses findings, and identifies next steps.
- Next Sprint Tests Improvement: Insights from AI and the retrospective directly feed into the next Agile sprint, allowing rapid testing of small, measurable improvements.
This creates a powerful “analytical flywheel”, a continuous feedback loop of AI-powered insights, Agile iteration, and measurable impact. This is great in allowing HR to become truly data-driven, responsive, and strategic.
ValueX2: Doubling Down on HR’s Impact
Generative AI prompts multiplied onto Agile HR rituals generate not just value, but ValueX2, a multiplier effect that accelerates the impact of HR, with a focus on AI in HR analytics:
- From Reactive to Predictive: Using AI in HR analytics provides HR with a predictive capacity that allows for proactive-based strategies.
- From Intuition to Insight: Decisions become data-driven with a hard data business case, through HR’s analytics.
- From Administrative to Strategic: HR can apply the money saved through the automated data gathering and analytics process to thinking strategically.
- From Cost Center to Growth Engine: By producing clear data that measures ROI “quick wins”, HR becomes the clear organizational growth vehicle.
Finally, and importantly, our ICAgile Agility in HR brings these approaches together to help you create the best workflow that allows HR Teams to create their pipeline, respectively, to focus, design sprint experiments, and even develop a personal playbook to create immediate measures of impact, always making sure there are tangible business benefits.
Closing Thought: The Art and Science of HR Analytics with AI
Utilizing AI in HR analytics is an art and a science. The “science” involves data, algorithms, and prompt writing. The “art” is framing the best questions, understanding nuanced responses, and converting data into meaningful human stories and proactive decisions.
You can use as few as three of the prompts above today. Watch as response rates, time-to-hire, quality-of-hire, or employee sentiment metrics change. Clear instructions and an Agile rhythm turn Generative AI into more than a toy – it becomes an essential strategic partner for HR as it moves from an order-taking service desk to a data-driven growth engine.
The future of HR is now, and with smart prompts and agile practices, you will realize ValueX2 at every turn.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do AI prompts for HR analytics save considerable time?
A: Absolutely. HR teams that use analytics prompts indicate a systematic reduction of time using manual methods of data processing and producing reports of 30% to 50%. This releases literally hours and hours monthly for strategic initiatives using AI in HR analytics.
Q: Are “prompts for engineers for HR analytics” merely a fancy term for data queries?
A: No. It is vastly more complicated than that. Good analytical AI prompts provide context, specify data structures, identify intended outcomes, highlight any constraints or limitations, and clarify the output format for complicated data analyses and predictions. These steps are critically important for effective AI in HR analytics.
Q: Can Generative AI introduce or exacerbate bias in HR analytics?
A: Any AI system can reflect and amplify biases in its training data. There is no definitive form of bias mitigation; it still involves active testing to identify unfairness in the AI-generated interpretive outputs. This mitigation requires objective analytical frameworks. Human guidance and oversight are needed when making decisions based on AI outputs in HR analytics.
Q: Will AI replace HR analytics professionals?
A: It is more likely that AI will enhance its performance. AI will conduct labor-intensive data tasks while allowing HR professionals to interpret complicated patterns, establish a strategic narrative, and persuade organizational leaders with evidence-based conclusions in HR analytics.
Q: How can we demonstrate the ROI of investing in AI and Agile HR to finance?
A: Track and present clear business cases using metrics like reduced time-to-hire, decreased cost-per-hire, improved quality-of-hire, lower regrettable attrition, and increased employee engagement scores. The quantitative improvements will speak volumes for AI in HR analytics.

Sagar is an HR Agile Coach & Business Agility Consultant with 15+ years of experience in HR functions at small and large multinational corporations. He has been running an HR consulting firm for the last few years, focusing on leveraging agile methods to increase business efficiency.
Sagar is an authorized instructor for ICAgile Agility in HR (ICP-AHR) and Business Agility Foundations (ICP – BAF) training courses. He has considerable experience in coaching and training on applying agile practices for his clients, primarily HR departments. He also provides consulting for HR for Agile and Agile for HR transformation to corporates.






